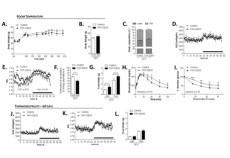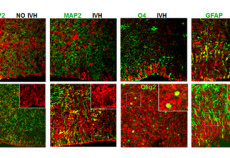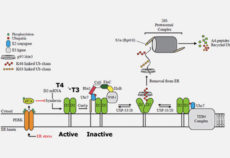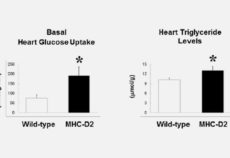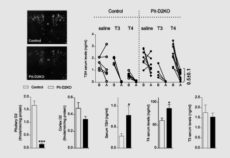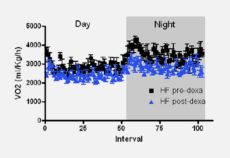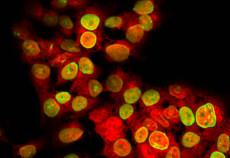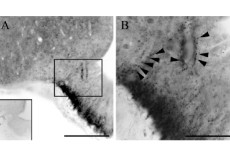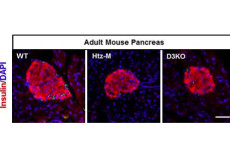
Maternal inheritance of Dio3 gene Allele affects mouse b-cells. PMID: 24885572
Dio3 is the most distal gene of the imprinted Dlk1-Dio3 gene locus and is expressed according to parental origin. Dio3 encodes the type 3 deiodinase (D3), a thioredoxin-fold like containing selenoenzyme that inactivates thyroid hormone and dampens thyroid hormone signaling. Here we used heterozygous animals with disruption of the Dio3 gene to study the allelic […]