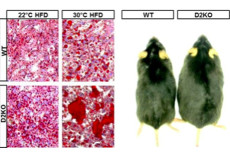
D2KO causes obesity, glucose intolerance and liver steatosis. PMID: 21335378
OBJECTIVE: Thyroid hormone accelerates energy expenditure; thus, hypothyroidism is intuitively associated with obesity. However, studies failed to establish such a connection. In brown adipose tissue (BAT), thyroid hormone activation via type 2 deiodinase (D2) is necessary for adaptive thermogenesis, such that mice lacking D2 (D2KO) exhibit an impaired thermogenic response to cold. Here we investigate […]