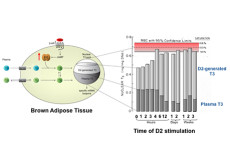
Emerging Therapies in Hypothyroidism
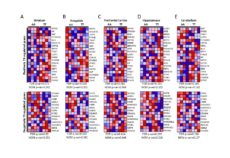
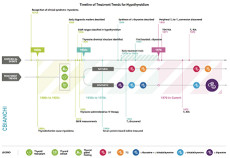
Levothyroxine (LT4) is effective for most patients with hypothyroidism. However, a minority of the patients remain symptomatic despite the normalization of serum thyrotropin levels. Randomized clinical trials including all types of patients with hypothyroidism revealed that combination levothyroxine and liothyronine (LT4+LT3) therapy is safe and is the preferred choice of patients versus LT4 alone. Many […]